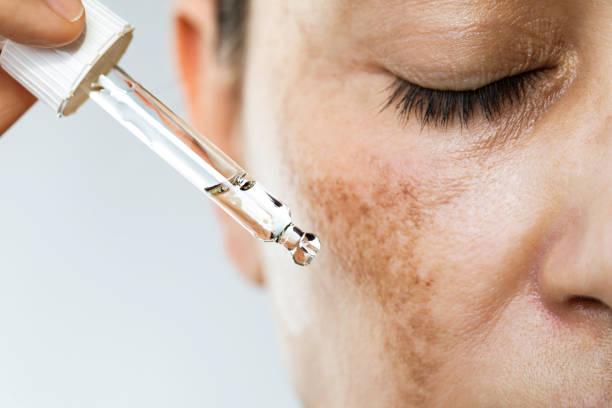
[I]f you have noticed dark spots or patches on your skin that don’t seem to go away, you might be dealing with melasma. This common skin condition can be managed with the right knowledge and tools.
In this article, we’ll explore what melasma is, its causes and symptoms, and the various ways you can manage it, including lifestyle changes, skincare routines, and professional treatments.
Table of Contents
What exactly is Melasma?
“Melasma is a skin condition that causes patches to appear, typically on the face, that are darker than a person’s skin tone. It may affect between 1.5–33% of people depending on the population.
Melasma can be found primarily in individuals with light brown skin to darker skin tones, especially in areas with high sun exposure. Women are particularly susceptible to melasma, and it can appear as brown patches on the face, especially the cheeks, nose bridge, and forehead.” MedicalNewsToday
Melasma, also known as pregnancy mask or chloasma, is a skin condition that causes brown or greyish-brown patches on the face, typically on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and chin. It occurs when the body produces too much melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour.

While it’s not harmful, melasma can be frustrating and difficult to manage, especially if it affects your self-confidence.
Factors that cause melasma
Several factors can contribute to the development of melasma, including:
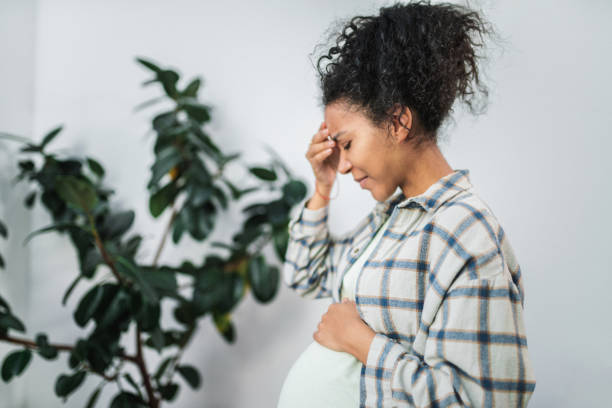
- Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills
- Sununun exposure
- Heat exposure, like using hot saunas or steam rooms
- Genetics
- Certain medications, such as oral contraceptives, blood pressure medication, and antimalarial drugs
- Understanding the potential causes of melasma can help you better manage it and prevent it from getting worse.
How does it impact the skin?
Hyperpigmentation
The skin produces excess melanin, leading to dark spots or patches on the skin.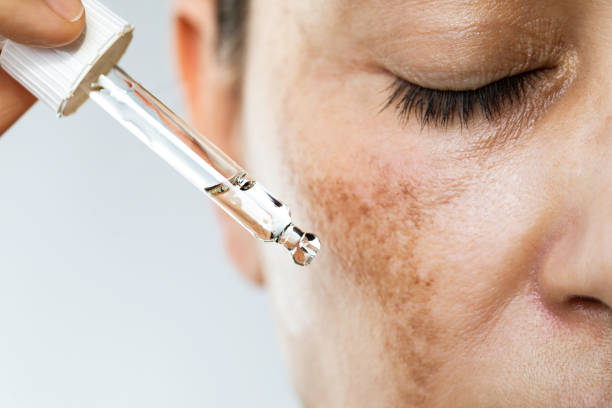
Skin Texture Changes
Melasma can cause the skin to become rough, uneven, or textured.
Thinning of the Skin
Over time, melasma can cause the skin to become thinner, making it more vulnerable to damage from the sun and other environmental factors.
Increased Sensitivity
People with melasma may find that their skin is more sensitive to irritants like sunlight, heat, and cosmetics.
How do you know if you have melasma?
Here are some common signs and symptoms to look out for:
- Dark, discoloured patches on the skin, typically on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and chin
- Patches that may appear blotchy or uneven
- Symmetrical Patches, meaning they appear on both sides of the face
- Patches that darken or lighten with sun exposure
- Patches that are more noticeable during summer months or after sun exposure
How to manage Melasma
- Protect your skin from the sun by wearing sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher and protective clothing, like wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeved shirts.
- Avoid heat exposure, like hot saunas or steam rooms, as heat can exacerbate melasma.
- Use skin-lightening products, like hydroquinone, kojic acid, or vitamin C serums, under the guidance of a dermatologist.
Lifestyles changes to manage Melasma
- Eat a balanced diet that includes antioxidant-rich foods, like berries, green tea, and nuts, to promote skin health.
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol, as they can exacerbate melasma.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, as dehydration can worsen skin conditions
- Practice stress-reducing activities, like yoga or meditation, as stress can worsen melasma.
Effective skincare routine to manage Melasma
Use a gentle, non-irritating cleanser
Choose a cleanser that is designed for sensitive skin and does not contain harsh ingredients like sulfates or alcohol.
Apply sunscreen every day
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, and reapply every two hours if you are in the sun.
Use a vitamin C serum
Vitamin C helps to brighten the skin and reduce the appearance of dark spots.
Possible professional treatment of severe Melasma
Chemical peels
A dermatologist applies a chemical solution to the skin to remove the top layer of damaged skin cells, revealing smoother, more even-toned skin.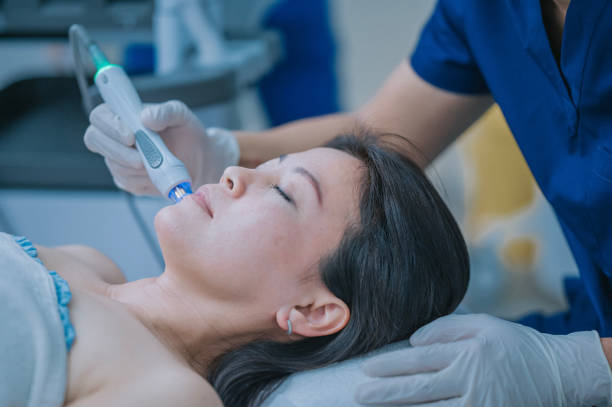
Laser therapy
A laser is used to destroy the excess pigment in the skin, reducing the appearance of dark spots.
Microdermabrasion
A device is used to gently exfoliate the skin, removing the top layer of dead skin cells and stimulating new cell growth.
In conclusion, melasma can be frustrating and challenging to manage, but with the right knowledge and treatment, it can be effectively controlled.
Remember to be patient and consistent in your approach to managing melasma, and don’t hesitate to consult a dermatologist if you have any concerns or if your symptoms persist.
Photo Credit: GETTY